|
upm
1.7.1
Sensor/Actuator repository for libmraa (v2.0.0)
|
|
upm
1.7.1
Sensor/Actuator repository for libmraa (v2.0.0)
|
API for the BMX055 9-axis Sensor Module. More...
The BMX055 is an integrated 9-axis sensor for the detection of movements and rotations and magnetic heading. It comprises the full functionality of a triaxial, low-g acceleration sensor, a triaxial angular rate sensor and a triaxial geomagnetic sensor.
The BMX055 senses orientation, tilt, motion, acceleration, rotation, shock, vibration and heading in cell phones, handhelds, computer peripherals, man-machine interfaces, virtual reality features and game controllers.
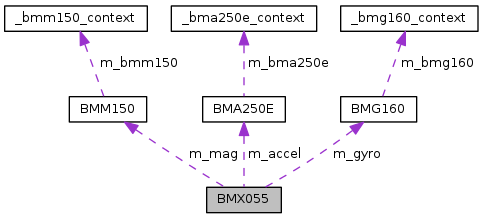
The BMX055 is essentially 3 separate devices in one: the BMA250E Accelerometer, the BMG160 Gyroscope, and the BMM150 Magnetometer. They are completely independent of each other.
This driver provides a very simple interface to these 3 devices. If finer control is desired, you should just use the separate BMA250E, BMG160, and BMM150 device classes directly. This driver simply initializes all three devices, and provides a mechanism to read accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer data from them.
Public Member Functions | |
| BMX055 (int accelBus=BMA250E_DEFAULT_I2C_BUS, int accelAddr=BMA250E_DEFAULT_ADDR, int accelCS=-1, int gyroBus=BMG160_DEFAULT_I2C_BUS, int gyroAddr=BMG160_DEFAULT_ADDR, int gyroCS=-1, int magBus=BMM150_DEFAULT_I2C_BUS, int magAddr=BMX055_DEFAULT_MAG_I2C_ADDR, int magCS=-1) | |
| ~BMX055 () | |
| void | update () |
| void | initAccelerometer (BMA250E_POWER_MODE_T pwr=BMA250E_POWER_MODE_NORMAL, BMA250E_RANGE_T range=BMA250E_RANGE_2G, BMA250E_BW_T bw=BMA250E_BW_250) |
| void | initGyroscope (BMG160_POWER_MODE_T pwr=BMG160_POWER_MODE_NORMAL, BMG160_RANGE_T range=BMG160_RANGE_250, BMG160_BW_T bw=BMG160_BW_400_47) |
| void | initMagnetometer (BMM150_USAGE_PRESETS_T usage=BMM150_USAGE_HIGH_ACCURACY) |
| void | getAccelerometer (float *x, float *y, float *z) |
| std::vector< float > | getAccelerometer () |
| void | getGyroscope (float *x, float *y, float *z) |
| std::vector< float > | getGyroscope () |
| void | getMagnetometer (float *x, float *y, float *z) |
| std::vector< float > | getMagnetometer () |
Protected Attributes | |
| BMA250E * | m_accel |
| BMG160 * | m_gyro |
| BMM150 * | m_mag |
| BMX055 | ( | int | accelBus = BMA250E_DEFAULT_I2C_BUS, |
| int | accelAddr = BMA250E_DEFAULT_ADDR, |
||
| int | accelCS = -1, |
||
| int | gyroBus = BMG160_DEFAULT_I2C_BUS, |
||
| int | gyroAddr = BMG160_DEFAULT_ADDR, |
||
| int | gyroCS = -1, |
||
| int | magBus = BMM150_DEFAULT_I2C_BUS, |
||
| int | magAddr = BMX055_DEFAULT_MAG_I2C_ADDR, |
||
| int | magCS = -1 |
||
| ) |
BMX055 constructor.
This device can support both I2C and SPI. For SPI, set the addr to -1, and specify a positive integer representing the Chip Select (CS) pin for the cs argument. If you are using a hardware CS pin (like edison with arduino breakout), then you can connect the proper pin to the hardware CS pin on your MCU and supply -1 for cs. The default operating mode is I2C.
| accelBus | I2C or SPI bus to use. -1 to skip initializing this device. |
| accelAddr | The address for this device. -1 for SPI. |
| accelCS | The gpio pin to use for the SPI Chip Select. -1 for I2C or for SPI with a hardware controlled pin. |
| gyroBus | I2C or SPI bus to use. -1 to skip initializing this device. |
| gyroAddr | The address for this device. -1 for SPI. |
| gyroCS | The gpio pin to use for the SPI Chip Select. -1 for I2C or for SPI with a hardware controlled pin. |
| magBus | I2C or SPI bus to use. -1 to skip initializing this device. |
| magAddr | The address for this device. -1 for SPI. |
| magCS | The gpio pin to use for the SPI Chip Select. -1 for I2C or for SPI with a hardware controlled pin. |
| void update | ( | void | ) |
Update the internal stored values from sensor data.
| void initAccelerometer | ( | BMA250E_POWER_MODE_T | pwr = BMA250E_POWER_MODE_NORMAL, |
| BMA250E_RANGE_T | range = BMA250E_RANGE_2G, |
||
| BMA250E_BW_T | bw = BMA250E_BW_250 |
||
| ) |
Initialize the accelerometer and start operation. This function is called from the constructor so will not typically need to be called by a user unless the device is reset or you want to change these values.
| pwr | One of the BMA250E_POWER_MODE_T values. The default is BMA250E_POWER_MODE_NORMAL. |
| range | One of the BMA250E_RANGE_T values. The default is BMA250E_RANGE_2G. |
| bw | One of the filtering BMA250E_BW_T values. The default is BMA250E_BW_250. |
| void initGyroscope | ( | BMG160_POWER_MODE_T | pwr = BMG160_POWER_MODE_NORMAL, |
| BMG160_RANGE_T | range = BMG160_RANGE_250, |
||
| BMG160_BW_T | bw = BMG160_BW_400_47 |
||
| ) |
Initialize the gyroscope and start operation. This function is called from the constructor so will not typically need to be called by a user unless the device is reset or you want to change these values.
| pwr | One of the BMG160_POWER_MODE_T values. The default is BMG160_POWER_MODE_NORMAL. |
| range | One of the BMG160_RANGE_T values. The default is BMG160_RANGE_250. |
| bw | One of the filtering BMG160_BW_T values. The default is BMG160_BW_400_47. |
| void initMagnetometer | ( | BMM150_USAGE_PRESETS_T | usage = BMM150_USAGE_HIGH_ACCURACY | ) |
Initialize the magnetometer and start operation. This function is called from the constructor so will not typically need to be called by a user unless the device is reset or you want to change these values. This method will call BMM150::setPresetMode() with the passed parameter.
| usage | One of the BMM150_USAGE_PRESETS_T values. The default is BMM150_USAGE_HIGH_ACCURACY. |
| void getAccelerometer | ( | float * | x, |
| float * | y, | ||
| float * | z | ||
| ) |
Return accelerometer data in gravities. update() must have been called prior to calling this method.
| x | Pointer to a floating point value that will have the current x component placed into it. |
| y | Pointer to a floating point value that will have the current y component placed into it. |
| z | Pointer to a floating point value that will have the current z component placed into it. |

| std::vector< float > getAccelerometer | ( | ) |
Return accelerometer data in gravities in the form of a floating point vector. update() must have been called prior to calling this method.

| void getGyroscope | ( | float * | x, |
| float * | y, | ||
| float * | z | ||
| ) |
Return gyroscope data in degrees per second. update() must have been called prior to calling this method.
| x | Pointer to a floating point value that will have the current x component placed into it. |
| y | Pointer to a floating point value that will have the current y component placed into it. |
| z | Pointer to a floating point value that will have the current z component placed into it. |

| std::vector< float > getGyroscope | ( | ) |
Return gyroscope data in degrees per second in the form of a floating point vector. update() must have been called prior to calling this method.

| void getMagnetometer | ( | float * | x, |
| float * | y, | ||
| float * | z | ||
| ) |
Return magnetometer data in micro-Teslas (uT). update() must have been called prior to calling this method.
| x | Pointer to a floating point value that will have the current x component placed into it. |
| y | Pointer to a floating point value that will have the current y component placed into it. |
| z | Pointer to a floating point value that will have the current z component placed into it. |

| std::vector< float > getMagnetometer | ( | ) |
Return magnetometer data in micro-Teslas (uT) in the form of a floating point vector. update() must have been called prior to calling this method.

 1.8.11
1.8.11